In today’s digital landscape, technical SEO is the backbone of a successful website. While content and keywords are crucial, technical SEO ensures that search engines can properly access, crawl, and index your site, ultimately influencing how it appears in search results. This comprehensive technical SEO checklist covers essential technical SEO best practices, from optimizing your site’s structure and speed to implementing advanced schema markup. By following these guidelines, you can ensure that your website not only meets the foundational technical requirements but also stands out in the competitive search engine environment, leading to improved rankings and a better user experience.
Table of Contents
Create an XML Sitemap
Generate an XML Sitemap for your website which contains all the web pages that you want search engine crawlers to crawl and index. Make sure that correct URL’s are included for web pages in the XML Sitemap. For example: If you use https://www before your website name, make sure that all the URL’s in the sitemap follow this rule.
Also make sure to validate your sitemap.xml URL before moving ahead to submit the sitemap to Google and other search engine. This will help you to find out any sitemap related issues.
Link to Sitemap Validator tool
Submit your Sitemap to Search Engine Webmaster Tools
Once you have created the XML sitemap and checked that it contains the correct URL for each web page, move on to submit the XML Sitemap link to Google Search Console ,Bing Webmasters Tool. If you receive a large amount of traffic from China and Russia, submit your XML Sitemap to Baidu & Yandex Webmaster tools respectively.
Personally, I have found that submitting XML Sitemaps to Webmaster tools accelerates the process of crawling and indexing, especially for new websites.
Add a Robots.txt file
Make sure to add a robots.txt file and only disallow sub-directories and URL’s that you don’t want Google and other search engine bots to crawl. Check that you don’t block important CSS & Javascript resources that are critical for loading your web pages. Otherwise, this will prevent the web crawlers from crawling your CSS and Javascript files and this may result in missing these files and important content inside these files from being indexed and shown in Search Engine Result Pages.
Include your correct sitemap URL in your robots.txt file
Search engine crawlers first visits a website robots.txt file to see which URL’s and sub-directories they are allowed to crawl and which they aren’t. Including your website’s sitemap URL in the robots.txt file will help web crawlers to crawl and index those web pages.
If you have sub-domains, make sure to create robot.txt file for each sub-domain.
Once you have created your robots.txt file, make sure to use a robots.txt tester tool to find out if your robots.txt contains any errors.
Link to robots.txt tester tool
Create Hreflang Tag
If you have a multilingual website with two or more languages, make sure that you utilise the hreflang tags correctly to show web pages in relevant language in the SERP’s when someone searches for that topic. When showing web pages in the SERP’s, search engines take into account various factors to only show web pages in the searcher’s browser language and location.
There are three ways to implement hreflang correctly.
- The first way is to implement it by adding the hreflang tag in the HTML head section.
- The second method is by adding it to the http header section.
- The third and the last method is to add it to the sitemap.xml file for each URL.
It doesn’t matter which method you use out of the three, but make sure to test your Hreflang tags by using a Hreflang tags testing tool.
Make sure you follow the correct language and country naming convention as missing out on this will mess up your hard work. For example: If you have a website yourwebsite.com with separate sub-directories for different languages and country. You could create hreflang tag as below present on each web-page and their equivalent pages in another language.
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="en" href="https://yourwebsite.com/en" />
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="de" href="https://yourwebsite.com/de" />
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="zh" href="yourwebsite.com/zh" />
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="x-default" href="yourwebsite.com" />Please note that the x-default tag is optional but not compulsory. However, it’s useful for showing your websites to those users who don’t use any of the languages as described in hreflang tags. In this case it’s English, German and Chinese. So, if someone from France who uses French as a default browser language searches for something relevant to our website, the URL included in the x-default tag would be served by Google to them.
You can also put your English version or any other language version of the web page as the x-default based on your target country and importance. For example, if you have a business website whose main target market is Germany, you should put the German version of the web-page as the x-default.
Moreover, you can use the hreflang tag to show various versions of your english or any other language page to your website visitors in different countries.
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="en-US" href="https://yourwebsite.com/us" />
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="en-GB" href="https://yourwebsite.com/uk" />
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="en-CA" href="yourwebsite.com/ca" />
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="x-default" href="yourwebsite.com" />As you can see in the above hreflang code, various sub-directories are used to create customised versions of the web page according to various target audiences for better user engagement and conversions.
Please have a look at the Google’s hreflang documentation for more details.
404 Page
Make sure that you have a custom-designed 404 page on your website that helps your website users to navigate to important pages when lost. This helps in improving user experience, session duration and decreasing bounce rate. Also, assure that this 404 page is shown when an incorrect web address is entered in the browser. I have seen various sites especially custom-coded websites that don’t implement this correctly. For example: the 404 page will be displayed when you enter yourwebsite.com/abvhgf but when you enter yourwebsite.com/aiu.html you won’t see the 404 page template even though you can see the status code as showing 404 using http status checker tool.
HTML Lang Tag
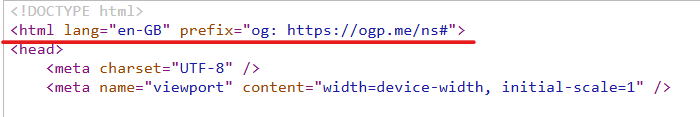
While Google doesn’t take into account HTML lang tag as a ranking factor, search engines like Bing do. However, it’s recommended to use the correct HTML lang tag on the website. This error generally exists on non-english wordpress websites. The easiest way to fix this issue is to go to your WordPress website Setting -> General -> Site Language and choose the appropriate language in which the website content is written.

Now after changing the site language, save the settings and open your Website. Now right-click and view page source to check if it’s now showing the updated site language.
Duplicate Content
Always make sure that the content on each of your web pages which includes text and images is unique, provides a new perspective to your readers and enhances your website’s technical SEO. However, you can surely use stock images on your website. Strictly try to avoid copying and pasting content from one web page to another as this will create duplicate content issues on your website which you check in Google Search Console in the Pages section under the Indexing tab. Additionally, you should also strictly avoid directly using content from other websites. Google and other search engines can easily track it and this will lead to a decrease in your website’s search engine ranking position. If the owners of the website find out that you have used their content without permission, this will lead to serious lawsuits.
To find duplicate content issues, you can also use Siteliner.
Javascript Rendering
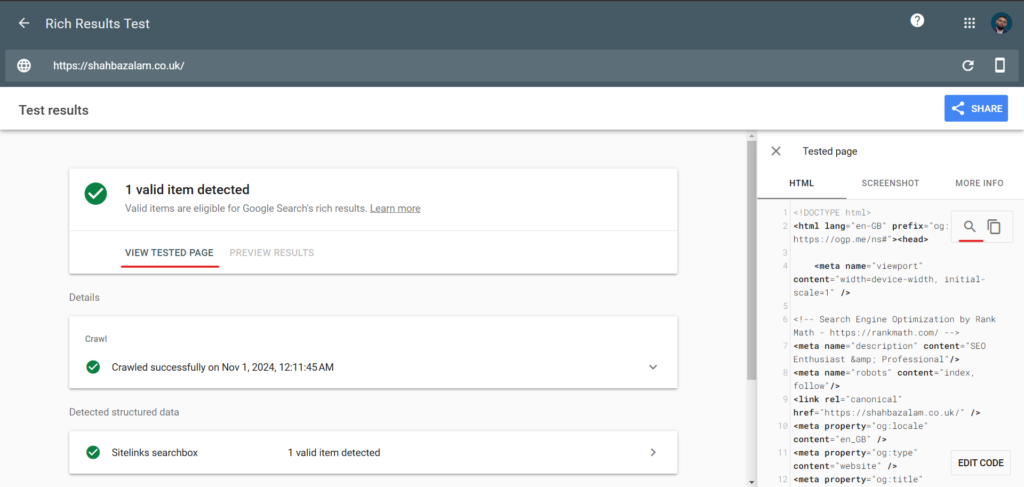
Some custom-coded websites especially those heavily reliant on Javascript have Javascript rendering issue. To diagnose this issue, use Google’s Rich Snippets Tool to find out javascript element that has problems in rendering & indexing. Click on “View Tested Page” as underlined in red in the below screenshot and then on the search icon. Then you can test for text content and see if its available in the Googlebot rendered version of your webpage.
Try to use HTML for the most important elements on a web page so that the crawlers can crawl your website and understand what your web page is all about even before the Javascript rendering process.
After the arrival of AI based searched engines and their inability to serve content rendered using javascript, its also wise to check if all the important content are served in the main HTML. To check this disable javascript on your web browser and load your website. To do this on Google chrome, open the developer Tools and click on the three dots on the top-right and Click on “Run command” as shown in the below screenshot.

Now type disable javascript in the input box and click on the option that says Disable Javascript as shown in the screenshot.

After this go to the Chrome tab where you had enables the Chrome dev tools and refresh the web-page. Now the web-page will load without Javascript. Its where you can check if all the critical content is loading without Javascript or if some of the important content are missing by comparing the web-page with and without Javascript.
Once you’re done with your task, go to dev tools where you had disabled javascript and now in the input box type “enable javascript” to enable it back again.

For better SEO optimisation, use Semantic HTML elements as it helps bots and crawlers get a better understanding of your webpage.
Schema Markup

While many tools provide basic schema generators, these may lack the nuanced details that schema.org’s extensive documentation offers. By following schema.org’s guidelines, you can create more comprehensive and accurate markups tailored to your website’s specific needs. Detailed schema implementation helps search engines recognize intricate elements on your site, from products and reviews to events and FAQ sections, leading to richer search results that attract more clicks.
Recommended Tools for Schema Validation
After implementing schema markup, validation is essential to ensure the code is error-free and correctly structured:
- Schema.org Validator: Visit validator.schema.org to verify your schema’s accuracy and syntax. This tool is particularly helpful in identifying any areas needing adjustments based on schema.org standards.
- Google Rich Results Test: Use Google’s Rich Results Test to see if your schema qualifies for enhanced search results, like ratings or review snippets. This test is especially useful for understanding how Google perceives and processes your structured data.
Pro Tip:
Whenever possible, go beyond generic schema markup tools. Instead, take time to refer to schema.org’s full documentation and customize your schema attributes. This approach not only improves the accuracy of your markups but also better aligns with search engines’ evolving requirements, resulting in richer and more engaging SERP displays.

